MOTS-c 10mg
$0.00
- when buying 5 units of goods 5% discount
- when buying 10 units of goods 8% discount
17 in stock
MOTS-c
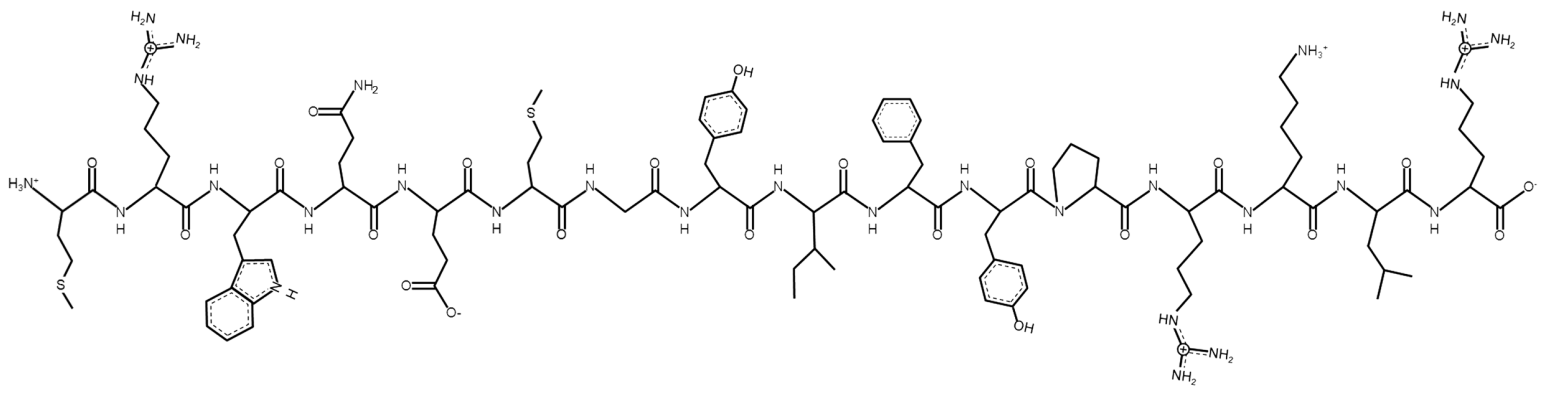
MOTS-C — The Mitochondrial Bio-Regenerator
Overview
MOTS-C (short for Mitochondrial ORF of the 12S rRNA Type-C) is a small bioactive peptide encoded within the mitochondrial genome — a rare example of mitochondria producing their own regulatory messenger.
Discovered in the early 2010s, MOTS-C has attracted major scientific interest for its roles in metabolic regulation, cellular resilience, and longevity research.
Unlike traditional peptides synthesized in the cytoplasm, MOTS-C originates directly from mitochondrial DNA (the 12S rRNA gene) and functions as a messenger between mitochondria and the nucleus, helping maintain energy balance, stress resistance, and metabolic homeostasis.
Structure and Biochemical Properties
-
Amino Acid Sequence: Met-Arg-Trp-Gln-Glu-Met-Gly-Tyr-Ile-Phe-Tyr-Pro-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg
-
Molecular Formula: C₁₀₁H₁₅₂N₂₈O₂₂S₂
-
Molecular Weight: 2174.64 g/mol
-
CAS Number: 1627580-64-6
-
Synonym: MT-RNR1 Peptide
-
Class: Mitochondrial-derived regulatory peptide
Biological Functions
MOTS-C acts as a metabolic “master switch”, influencing multiple signaling pathways:
-
AMPK activation: initiates the cellular “energy-saving mode,” encouraging fat oxidation and reducing glucose overload.
-
Metabolic reprogramming: improves mitochondrial efficiency and supports lipid utilization.
-
Neuroprotection: enhances cellular stress resistance through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory signaling.
-
Muscle preservation: supports mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle, counteracting sarcopenia.
-
Cellular stress balance: interacts with HSPs, GSK-3β, and JNK pathways, helping cells adapt to metabolic or oxidative challenges.
MOTS-C and Skeletal Muscle Metabolism
Research indicates that MOTS-C promotes healthy skeletal muscle function and endurance capacity.
In preclinical studies, it improved mitochondrial density, enhanced glucose uptake, and reduced myostatin expression — a protein that inhibits muscle growth.
These findings suggest that MOTS-C helps maintain muscle mass and energy utilization, particularly under metabolic stress or aging conditions.
MOTS-C and Lipid Metabolism
MOTS-C supports lipid homeostasis by:
-
Increasing fatty-acid oxidation
-
Enhancing mitochondrial respiration
-
Reducing diet-induced adiposity in experimental models
Animal studies demonstrated that MOTS-C administration mitigated high-fat-diet-induced obesity, regulated lipid intermediates such as sphingolipids and monoacylglycerols, and improved overall metabolic flexibility.
These effects are associated with activation of AMPK and nuclear gene expression that promote fat utilization and energy efficiency.
Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Homeostasis
Low MOTS-C levels have been correlated with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome markers in both animal and human studies.
In experimental settings, MOTS-C:
-
Improved glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity
-
Reduced hyperglycemia in diet-induced obesity models
-
Enhanced glucose uptake in skeletal muscle through mitochondrial-nuclear signaling
This peptide is being studied as a potential regulator of metabolic aging and a promising target in the research of type 2 diabetes and prediabetic states.
MOTS-C and Bone Health
Recent studies highlight a potential protective role in bone metabolism.
MOTS-C appears to enhance osteoblast differentiation, improve mineral density, and support bone regeneration in animal models.
By influencing gene expression involved in bone remodeling, it may contribute to maintaining skeletal integrity and reducing age-related bone loss.
Cardiovascular Research
MOTS-C has shown promise in supporting cardiovascular function under metabolic stress.
In laboratory studies, it:
-
Improved systolic and diastolic heart function
-
Restored myocardial efficiency and reduced fibrosis
-
Enhanced vascular endothelial performance
-
Attenuated diabetic cardiomyopathy by normalizing mitochondrial bioenergetics
Population-based research has also associated lower circulating MOTS-C levels with increased cardiovascular risk, suggesting its potential as a biomarker in heart-health studies.
MOTS-C and Longevity Research
MOTS-C has been identified as a key mitochondrial-derived longevity factor.
Certain genetic variants within the MT-RNR1 gene (such as m.1382A>C) are associated with exceptional human longevity.
Experimental evidence suggests that MOTS-C enhances resilience to metabolic stress, promotes efficient energy utilization, and supports active aging through mitochondrial communication with nuclear DNA.
Safety and Research Use
MOTS-C is supplied for research and educational purposes only.
It is not intended for human or veterinary use, not approved as a dietary supplement, and should be handled only by qualified professionals in a controlled laboratory setting.
Summary
MOTS-C represents a new class of mitochondrial-encoded peptides with wide-ranging research potential in the study of:
-
Metabolic adaptation
-
Insulin sensitivity and glucose regulation
-
Muscle preservation and physical endurance
-
Lipid metabolism and mitochondrial efficiency
-
Longevity and age-related decline
-
Bone and cardiovascular health
It functions not as a stimulant, but as a cellular re-educator — restoring natural energy balance and cellular harmony.
Selected References
-
Lee C., Zeng J., Drew B.G. et al. The mitochondrial-derived peptide MOTS-c promotes metabolic homeostasis and reduces obesity and insulin resistance. Cell Metabolism. 2015;21(3):443–454. PubMed: 25738459
-
Reynolds J.C. et al. MOTS-c is an exercise-induced mitochondrial peptide that increases physical performance. Cell Metabolism. 2021;33(11):2174–2187. PubMed: 34600713
-
Kim S.J., Miller B., Hwang A.B. et al. Mitochondrial-encoded MOTS-c prevents diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance in mice. Nature Communications. 2019;10:4187. PubMed: 31541111
-
Du C., Wang C., Zhang H. et al. MOTS-c improves osteoporosis by promoting bone formation and inhibiting resorption. Aging Cell. 2021;20(6):e13386. PubMed: 34060147
-
Yadav A., Singh S., Srivastava A. MOTS-c: A mitochondrial micropeptide linking exercise, metabolism, and longevity. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2022;13:862740. PubMed: 35547533
-
Meng J., Yang S. et al. Circulating MOTS-c levels are associated with cardiovascular health in metabolic disorders. Metabolism. 2023;145:155608. PubMed: 36870021
Product Use: THIS PRODUCT IS STRICTLY FOR
SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY. It should only be used in laboratory
settings. All product information on this website is provided solely for
educational purposes. The law strictly prohibits introducing this product into
the body of humans or animals. Only licensed professionals should handle this
product. This product is not a drug, food, or cosmetic and should not be
improperly classified or used as such.



Reviews
Clear filtersThere are no reviews yet.